


Like from the latin word intellegere = recognize, we would like to recognize from imaging how molecular biology in cells is unfolded. To interrogate genomic expression, single cell sequencing is currently the action of choice, while for 3D fluorescence, novel light sheet microscopy offers unprecedent imaging speed at lowest phototoxicity. We use these technologies in conjunction to explore the phenotype-genotype domain space and ultimately model different gene expression of patient organoids by imaging only. To correlate these big data matrices, deep learning classification became indispensable and finally drive our understanding in different aspects of therapy research and precision medicine at the Charité/ BIH. For details see https://iimaging.org/
Advanced automated light sheet microscopy and single cell sequencing are primed in the intelligent imaging lab to compare morphologies with different expression. With dual top objective geometries we apply stage-scanning modes for fast 3D image screening or acquisition of organoids in hydrogel droplets while further subsequent confocal imaging adds resolution. We are determined to automated the whole process of 3D spotting of organoids to droplet respiration, followed by single cell acid nucleic library generations. Especially, massive imaging over time demands for intelligent solution, namely deep learning algorithms, to selectively save and identify relevant information from those volumetric heterogenous data.

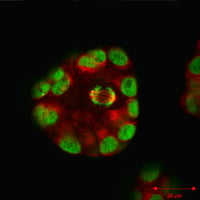
MCF10A breast spheroids, actin (red) and nuclei (green) staining
We engineered single cell as well as nuclei RNA/ATAC sequencing libraries from different tissues derived from patients material directly or from their derived organoids. Here, we specialized on protocols for lung and pancreas biopsies adapted to high autolytic properties after tissue resection. Beside these wet lab challenges, the intelligent imaging group studies morphological-cellular features correlating with the different gene expression profiles. Ideally, assuming a sufficient collection size that a phenotypic picture of tissues or organoids holistically inform us about the genetic makeup. In essence, we are employing single cell sequencing to understand different disease entities (cancer) on cellular scale.
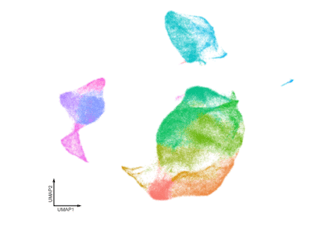
UMAP clustering example of high-dimensional single cell sequencing data
We do utilize the way artificial deep neural networks learn to recognize and reconstruct patterns in input data. This approach to single cell genomics datasets allows the de novo identification of functional gene sets, master regulator genes and housekeeping genes from any kind of tissue origin. Precise partitioning into cell types or sub clones in cancer tissues can be improved by introducing class-specific filters of measured modalities (images or clinical diagnostic parameters). Ultimately, tissue or organoid images should contain all features learnt in deep neural networks to enable seamless disease prediction and therapy management.

Christian Conrad graduated in Biology at the University Freiburg and received his PhD in Bioinformatics at the University Heidelberg. In 2018, he moved to the Charité/BIH where he was appointed as Professor for Intelligent Imaging.
Prof. Dr. Christian Conrad
Group leader Intelligent Imaging
Post Address:
Charité - Campus Charité Mitte | Charitéplatz 1 | 10117 Berlin | Germany
Visiting Address:
Rahel Hirsch Center | Luisenstraße 65 | 10117 Berlin
Level 02, Part B, room 217
Single-Nucleus and In Situ RNA-Sequencing Reveal Cell Topographies in the Human Pancreas.
Tosti L, Hang Y, Debnath O, Tiesmeyer S, Trefzer T, Steiger K, Ten FW, Lukassen S, Ballke S, Kühl AA, Spieckermann S, Bottino R, Ishaque N, Weichert W, Kim SK, Eils R, Conrad C.
Gastroenterology. 2021 Mar;160(4):1330-1344.e11.
Original publication PMID: 33212097
COVID-19 severity correlates with airway epithelium-immune cell interactions identified by single-cell analysis.
Chua RL, Lukassen S, Trump S, Hennig BP, Wendisch D, Pott F, Debnath O, Thürmann L et al.
Nat Biotechnol. 2020 Aug;38(8):970-979.
Original publication PMID: 32591762
Single-cell analysis of patient-derived PDAC organoids reveals cell state heterogeneity and a conserved developmental hierarchy.
Krieger TG, Le Blanc S, Jabs J, Ten FW, Ishaque N, Jechow K, Debnath O, Leonhardt CS, Giri A, Eils R, Strobel O, Conrad C.
Nat Commun. 2021 Oct 5;12(1):5826.
Original publication PMID: 34611171
Gene set inference from single-cell sequencing data using a hybrid of matrix factorization and variational autoencoders.
Lukassen S, Ten FW, Lukas A, Eils R, Conrad C.
Nat Mac Intell. 2020 Dec 7;2(12):800-809.
Original publication doi: 10.1038/s42256-020-00269-9
Katharina Jechow
Staff scientist
katharina.jechow@charite.de
Robert Lorenz Chua
Doctoral student
robert-lorenz.chua@charite.de
Timo Trefzer
Doctoral student
timo.trefzer@charite.de
Dr. Sören Lukassen
Postdoc
soeren.lukassen@charite.de
Foo Wei Ten
Doctoral student
foo-wei.ten@charite.de
Dr. Christian Conrad
Group leader
christian.conrad@bihealth.de
Dr. Luca Tosti
Postdoc
luca.tosti@charite.de
Dr. Teresa Gabriela Krieger
Postdoc
teresa.krieger@charite.de
Dr. Li-Ling
Postdoc
l.yang@dkfz-heidelberg.de
Adrian Huck
Student
adrian.huck@charite.de
Johannes Liebig
Doctoral student
johannes.liebig@charite.de
Alexander Sudy
Doctoral student
alexander.sudy@charite.de
Dr. Agata Rakszewska
Postdoc
agata.rakszweska@charite.de
Lukas Adam
Student
lukas.adam@charite.de

The Digital Health Center once again organises the INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON SYSTEMS BIOLOGY OF HUMAN DISEASE – SBHD 2025 in Berlin from June 16-18. Don’t miss this opportunity to participate in a

Our colleagues at Vanderbilt University organise the 16th INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON SYSTEMS BIOLOGY OF HUMAN DISEASE – SBHD 2024 this year from June 10-12. Don’t miss the opportunity to participate

Am 11.10.2023 wurde Prof. Roland Eils im Tagesspiegel als einer der 100 wichtigsten Köpfe der Hauptstadt-Wissenschaft gewürdigt. So schreibt der Tagesspiegel: "Um Big Data dreht sich alles in der

The Lindau Nobel Laureate Meetings are annual conferences where some of the brightest minds in science converge to exchange knowledge, foster collaboration, and inspire the next generation of
The Hub for Innovations in Digital Health (HiDiH) brings together two independent sites of excellent research and development in Berlin and in Heidelberg. HIDIH’s major branch in Berlin is the Center for Digital Health at the Charité and the Berlin Institute of Health (BIH).
If we caught your attention, you are interested in our work and would like to get in touch with us, please contact us via franziska.mueller@bih-charite.de



